Data integration are meant to solve two primary problems.
- Unified data by creating a co-relation between data available in different applications.
- Unified View by allowing users to see a unified view of the business data without hopping from one application to another.
In this blog post, we will focus on Unified View. One of the shortcomings of achieving a unified view by data Integrations is data duplication. Even though the Master data is stored in one place, a copy of its subset exist in other applications in order to create a Unified view. This data needs to be synchronized and updated as the master data changes. In some scenario, the changes from downstream application might update the master data and other copies.
Often time Dynamics CE is used to maintain Customer data while Operation data and Financial data are maintained in another application. in order to access the data, users need to navigate to the relevant application and look up the data. As an example, you might have customer record and Order data in CRM but the invoice and payment data could be in another ERP system( AX, GP, SAP etc.).
In Dynamics 365 CE there are multiple ways to achieve Unified View without or with reduced duplicate data, let’s dive into what these solutions are and when to use them.
- Unified Service Desk: A.K.A USD is a Desktop application and is another interface to access Dynamics 365, USD is geared towards Customer Service Desk and Call center agent.
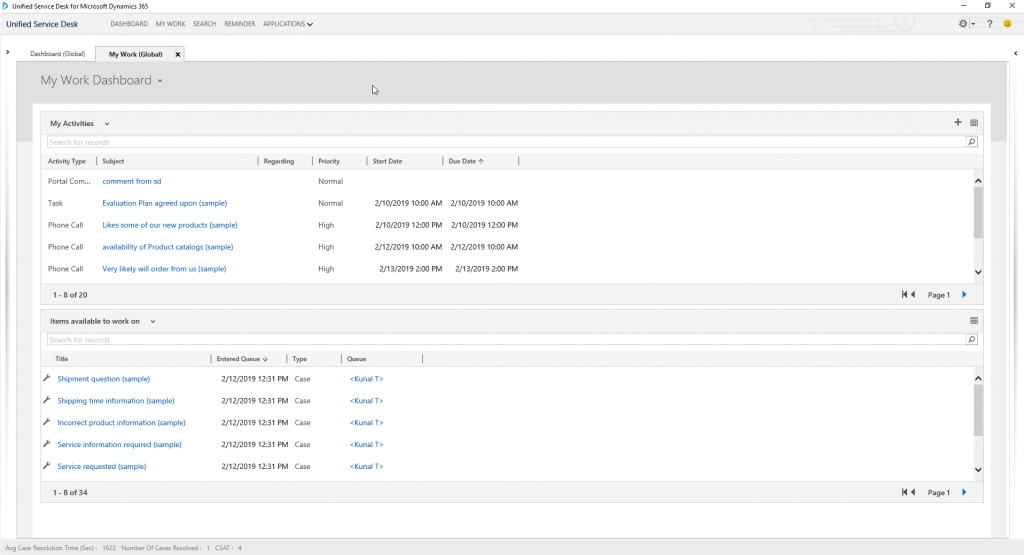
USD enables CTI integration which allows the system to be able to pull relevant customer information from CRM when Customer call comes in and it even loads the screen with Customer information from CRM and guides you through the call script based on the channel/issue.
Generally, CSR’s often need more information than what is available in CRM, in order to do so they need to navigate to other application. USD solves this problem by connecting other application into USD itself. Though the Enterprise is using multiple application to solve different business problems, CSR’s are presented with a Unified view of Customer Information in USD and is able to interact with all the application data without leaving Unified Service Desk.
Dynamics USD’s current version is 4.0. it has undergone a lot of changes since its initial release and lot many users are adopting it for the Customer service desk.
Unified Service Desk could be downloaded from here, It comes with a package deployer solution which contains sample package to jumpstart on using USD. Microsoft Business Apps MVP Neil Parkhurst has a lot of useful blogs on USD which could be very helpful.
2. Virtual entity: Virtual Entity is one of my favorite integration feature in Dynamics 365, it was introduced in 2017 (Version 9). Virtual entity enables external data to be surfaced in CRM without it be stored or Synchronized. Data is accessed and presented to the user at runtime.
Virtual entity is quite useful as related data could be present in Dynamics CE for reference without maintaining a copy of it, for example, you might have customer record and Order data in CRM but the invoice and payment data could be in another ERP system( AX, GP, SAP etc.). Using Virtual Billing and Payment information could be made available in Dynamics 365 CE.
Few things to consider is that Virtual entity is not security enabled and are organization owned, The data is only available in Read-Only mode. There has been some chatter about it being available in other modes in future but there hasn’t been any confirmation yet.
Virtual entities are made up of three main components, a data provider, a data source record, and a virtual entity. Dynamics 365 CE comes with an OData V4 Data Provider and additional provider could be custom built. Microsoft has also announced Azure Cosmos DB SQL API Data Provider for virtual entity and is currently in preview.
For Setting up Virtual Entity you can follow these steps.
With this, I will take a pause and continue on other available options for presenting unified View in Dynamics 365 in the next blog.