There are more and more installs of Microsoft On-premise data gateways to achieve Hybrid integrations scenarios. On-premise gateway provides a
quick and secure data transfer between on-premises data and Azure Cloud Services. In this blog, we will look into how we can monitor On-premise gateway Install, but before we get to it lets look into what is on-premise data gateway.
Whats is On-Premise Data gateway?
It allows you to build integrations which securely moves data between on-premise data sources and Azure Cloud Services.
Currently, on-Premise data gateway can be used to interact with Azure Service Bus, Azure Logic apps, Microsoft Flow, PowerApps, Power BI and Azure Analysis services on Azure. Here is the list of all different supported data sources.
How it works ?
On-Premise data gateway setup has two components. A piece of software(gateway service) needs to be installed and configured on an On-premise M/VM.
Another component is a gateway Resource in Azure which is connected to the gateway service running on Premise. Gateway resource needs to be in the same subscription and region as of the azure analysis service you are trying to connect with.
Both the component interacts and passes messages between On-premise and Azure cloud using an Azure service bus behind the scene. Once both components are configured you can use on -Premise data gateway for building hybrid integration.
Azure Logic apps, Microsoft Flow, Powerapps and Power BI connectors allows to create a connection using On-premise Data gateway.
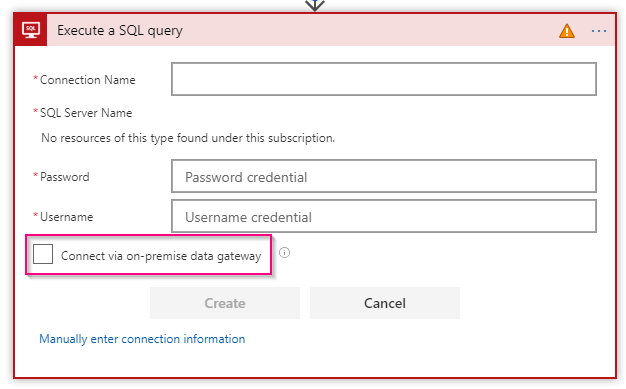
How to Monitor
One of the issues system admin often run into is that on-premise data gateway service is down, as such Hybrid integration is failing. This happens often while the On-premise VM is getting patched, updated, rebooted and on-premise data gateway doesn’t get started after. Let’s look into strategies you can adapt to avoid such scenarios:
Preventive :
- Configure on-premise gateway service to start upon System Start: do this to ensure service is started in case VM is rebooted or updated or patched.
- Service account: The Gateway service runs under an auto-created Virtual account but for finer control and management, you can switch it to use a managed Service account.

- High Availability: For high availability, Install the On-premise Gateway in cluster Mode, clusters allow gateway administrators to group gateways to avoid single point of failure in accessing on-premises data resources
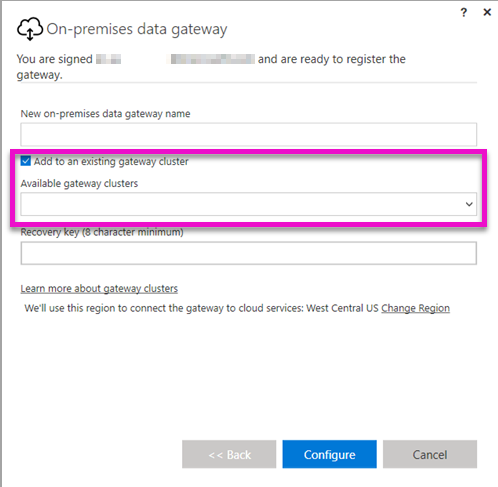
Monitoring:
- Logs :
- On-Premise Gateway Logs: All the on-premise gateway logs could be exported as a zip file from the on Premise Gateway Interface.
- Additional Logs: Additional Logging could be enabled which is useful in for Performance diagnostics.
- Pre-checks: Logic App and Flow integrations could be built to handle error for failure to connect using an on-premise gateway if the error occurs alerts could be sent to sysadmins.
- Performance Counters: On-Premise Gateway has a list of performance counters which could be utilized for tracking and evaluating the performance of the gateway, It’s a larger topic so I would cover it in my next blog(Monitoring Microsoft On-Premise Data Gateway Part II).